
7 Eukaryotic Cell Structure in Biological Science Picture Directory
Diagram Of Animal Cell Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They are different from plant cells in that they do contain cell walls and chloroplast. The animal cell diagram is widely asked in Class 10 and 12 examinations and is beneficial to understand the structure and functions of an animal.
6.1 Eukaryotic Cells Biology 110 PSU Dubois
Lynn Margulis Susan L. Lindquist Roger D. Kornberg Related Topics: On the Web: The University of Hawaiʻi Pressbooks - Biology - Eukaryotic Cells (Jan. 04, 2024) eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus.

identify and label each part of the eukaryotic cell
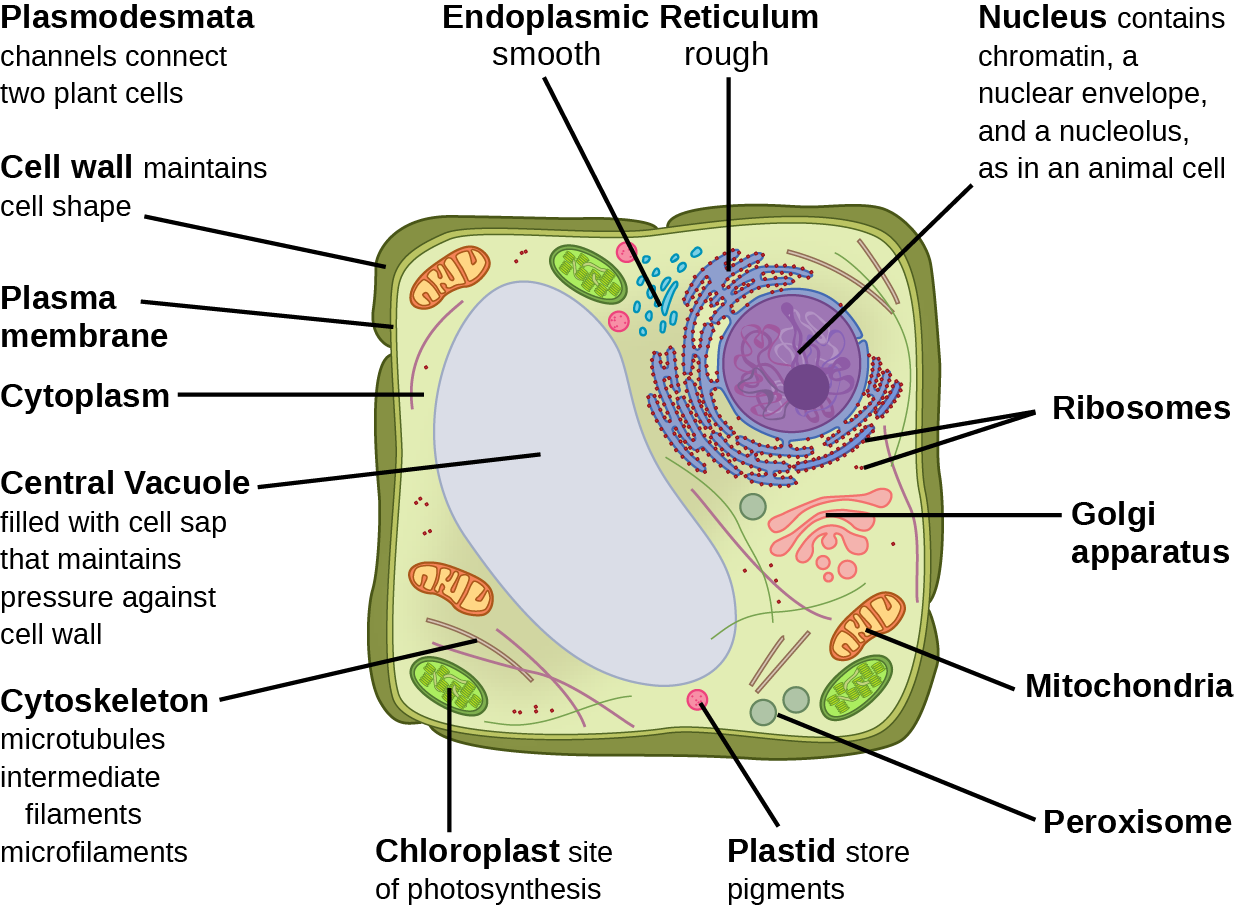
Diagram of a typical animal cell: Image modified from OpenStax Biology. Diagram of a typical plant cell:

2.2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Biology LibreTexts
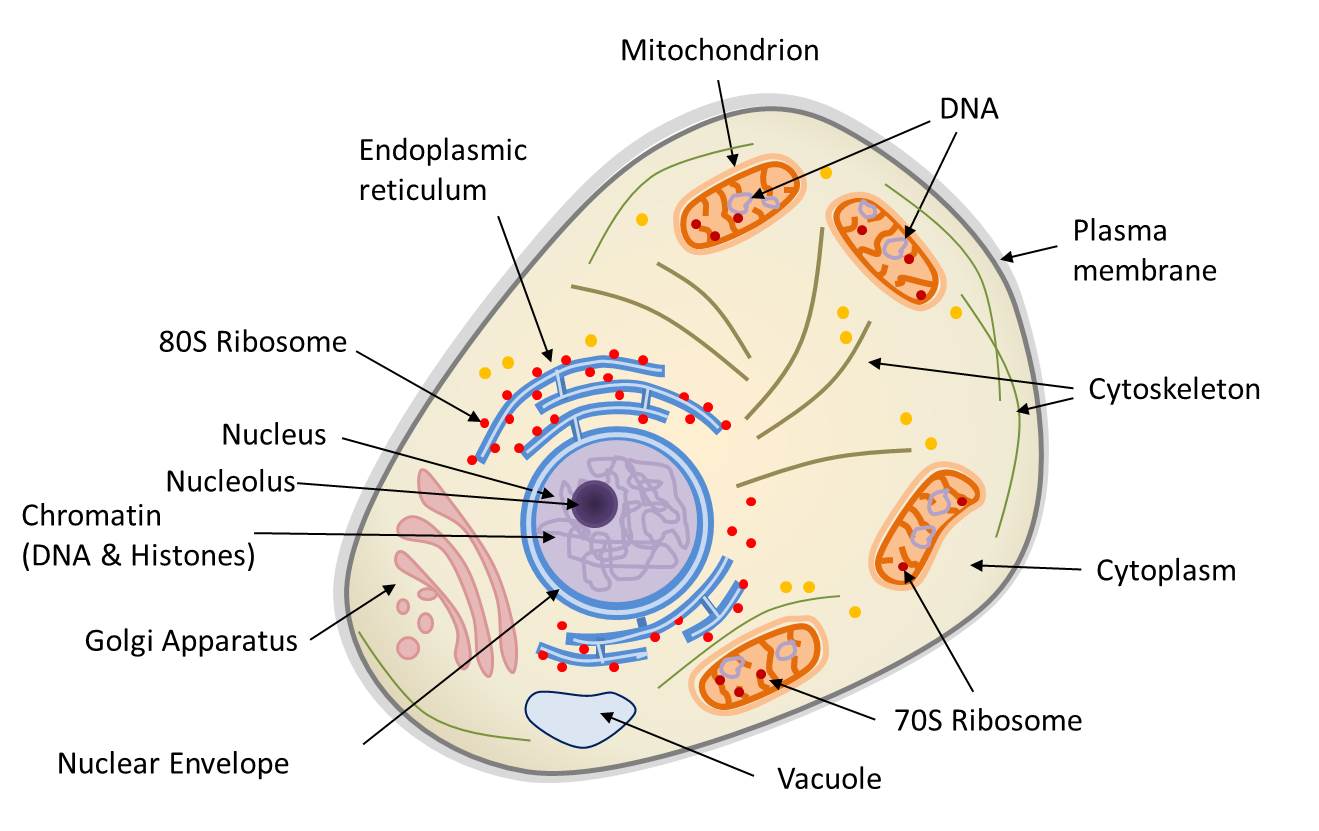
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it has a "true nucleus.".

Organization of Eukaryotic Cells
The Cell Wall. In Figure 3.3. 1 b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Fungal and protist cells also have cell walls.

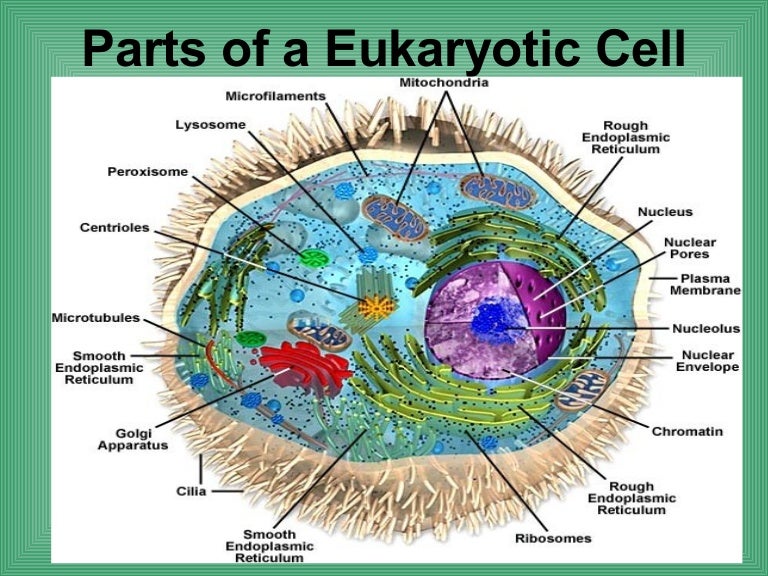
Ultrastructure of a eukaryotic cell an animal cell. Animal cell
The Plasma Membrane. Like prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane ( Figure 3.8) made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment. A phospholipid is a lipid molecule composed of two fatty acid chains, a glycerol backbone, and a phosphate group.
4.2 Parts Of A Eukaryotic Cell
The cell is the smallest functional unit within a living organism, which can function independently. It is made up of several types of organelles that allow the cell to function and reproduce. There are two general classes of cells that exist: the self-sustaining simple cells known as prokaryotic (bacteria and archaea) and the more complex dependent cells known as eukaryotic.

Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg
Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus, which means the cell's DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Therefore, the nucleus houses the cell's DNA and directs the synthesis of proteins and ribosomes, the cellular organelles responsible for protein synthesis. The nuclear envelope is a double-membrane structure that constitutes the outermost portion.

Eukaryotic Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Diagram Structure Types Conclusion Let us have a detailed overview of the animal cell, its types, diagram and structure. Animal Cell Definition "An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall and has a true, membrane-bound nucleus along with other cellular organelles." Explanation
Symbiosis and evolution at the origin of the eukaryotic cell
Summarize the functions of the major cell organelles Describe the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix At this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. Organelles allow for various functions to occur in the cell at the same time.

Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cellular Structures ALevel Biology
Definition A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.

eukaryotic cell images Biological Science Picture Directory
The cell wall. If you examine the diagram above depicting plant and animal cells, you will see in the diagram of a plant cell a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell.

Eukaryotic cell structure diagrams Biological Science Picture
Animal Cells versus Plant Cells. Each eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, a nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, and in some, vacuoles; however, there are some striking differences between animal and plant cells. While both animal and plant cells have microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs), animal cells also have.

The Eukaryotic Cell Micro Pinterest Cell structure and Teacher
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells, meaning they possess a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have cell walls, allowing for more flexibility in shape and movement. A plasma membrane encloses the cell contents of both plant and animal cells, but it is the outer coating of an animal cell.

Eukaryotic Cells The Cell MCAT Biology Review
An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Unlike the animal cell lacking the cell wall, plant cells have a cell wall.

Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
A tour of the animal cell by Biology Professor Dr. Jory. He explains each organelle's function including the nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear envelope, nuclear po.