
Be Kind To Your Feet VOICE
Anatomy of the foot Calcaneus (heel bone) Talus (ankle bone) Transverse tarsal joint Navicular bone Lateral cuneiform bone Intermediate cuneiform bone

Pin on Body (of) Work
Foot and ankle anatomy consists of 33 bones, 26 joints and over a hundred muscles, ligaments and tendons. This complex network of structures fit and work together to bear weight, allow movement and provide a stable base for us to stand and move on. The foot needs to be strong and stable to support us, yet flexible to allow all sorts of complex.
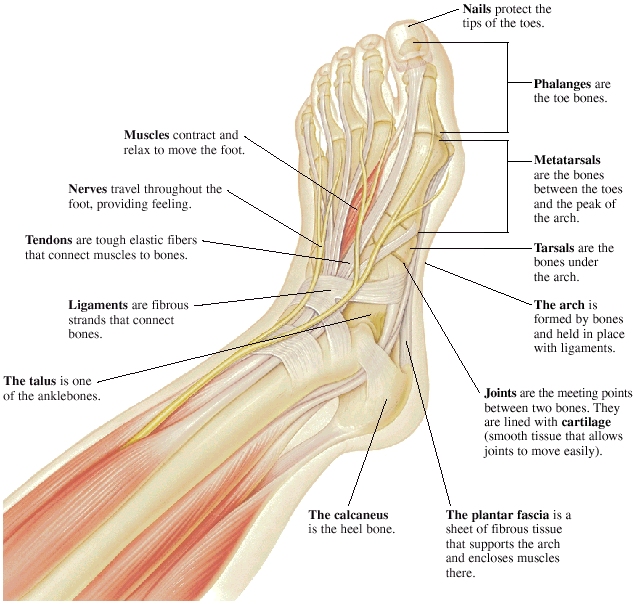
Foot, Parts of Anatomy and Physiology
The foot is one of the most complex parts of the body. It consists of 28 bones connected by many joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The foot is prone to many types of injuries. Foot pain and problems can cause pain and inflammation, limiting movement. Muscles contract and relax to move the foot.

Foot & Ankle Bones
Ankle anatomy The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. It is made up of three joints: upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints. The last two together are called the lower ankle joint.

Labeled Diagram Of The Foot Teenage Lesbians
Stress fractures Diabetic foot ulcers Last medically reviewed on April 13, 2015 The foot is the lowermost point of the human leg. The foot's shape, along with the body's natural.

Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle OrthoPaedia
Structure of the foot Conditions of the foot Summary The foot has a complicated anatomical structure with many parts, all of which have specific functions. Due to this complex structure,.

the body foot A1 English language teaching, English vocabulary
The midfoot is a pyramid-like collection of bones that form the arches of the feet. These include the three cuneiform bones, the cuboid bone, and the navicular bone. The hind foot forms the heel and ankle. The talus bone supports the leg bones (tibia and fibula), forming the ankle. The calcaneus (heel bone) is the largest bone in the foot.
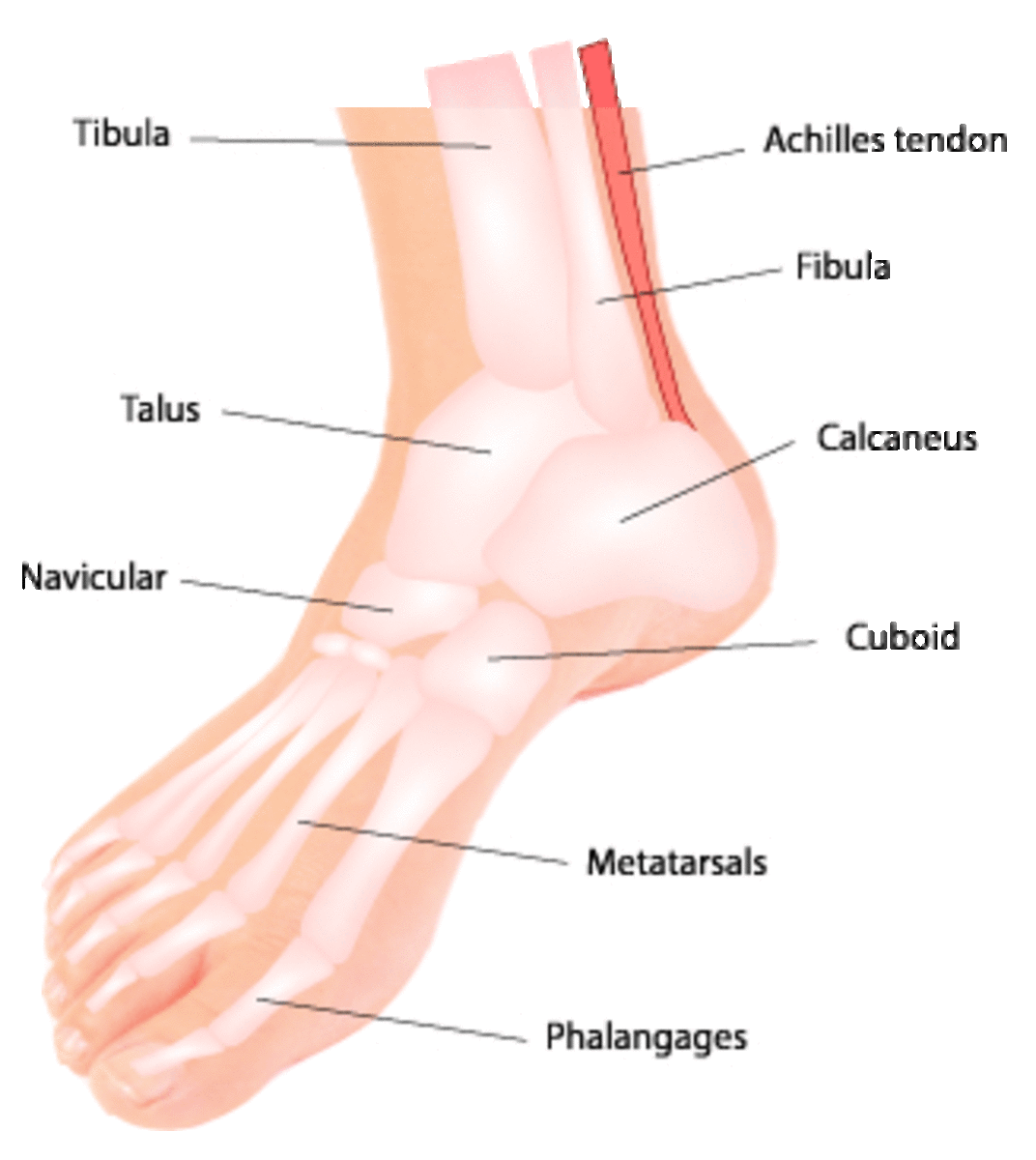
Foot Pain Natural Relief and Herbal Remedies HubPages
Navicular Cuboid Medial cuneiform Intermediate cuneiform Lateral cuneiform Some people may be born with an extra navicular bone ( accessory navicular) beside the regular navicular bone, on the inside of the foot. This is a normal anatomical variation seen in around 2.5% of the entire population of the US. Metatarsal Bones

Foot Anatomy 101 A Quick Lesson From a New Hampshire Podiatrist Nagy
Human body Skeletal System Bones of foot Bones of foot The 26 bones of the foot consist of eight distinct types, including the tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges, cuneiforms, talus, navicular,.

anatomy of the foot Ballet News Straight from the stage bringing
COVID-19

Diagram of The Foot 101 Diagrams
Bones. Nearly one-fourth of the body's bones are in our feet. The bones of the feet are: Talus - the bone on top of the foot that forms a joint with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and fibula. Calcaneus - the largest bone of the foot, which lies beneath the talus to form the heel bone. Tarsals - five irregularly shaped bones of.

Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle Foot and Ankle Diagram Anatomy of the
The foot is the region of the body distal to the leg that is involved in weight bearing and locomotion. It consists of 28 bones, which can be divided functionally into three groups, referred to as the tarsus, metatarsus and phalanges. The foot is not only complicated in terms of the number and structure of bones, but also in terms of its joints.

Parts of the feet and legs Grammar Tips
Foot (Anatomy): Bones, Ligaments, Muscles, Tendons, Arches and Skin Foot By: BD Editors Reviewed by: BD Editors Last Updated: July 25, 2017 Foot Definition The foot is a part of vertebrate anatomy which serves the purpose of supporting the animal's weight and allowing for locomotion on land.

Foot Anatomy and Function पाद pāda Elliots World
The foot can also be divided up into three regions: (i) Hindfoot - talus and calcaneus; (ii) Midfoot - navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms; and (iii) Forefoot - metatarsals and phalanges. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the bones of the foot - their bony landmarks, articulations, and clinical correlations.

Ankle+Anatomy+Muscles.jpg 1,166×1,500 pixels Anatomía del tobillo
Introduction A solid understanding of anatomy is essential to effectively diagnose and treat patients with foot and ankle problems. Anatomy is a road map. Most structures in the foot are fairly superficial and can be easily palpated. Anatomical structures (tendons, bones, joints, etc) tend to hurt exactly where they are injured or inflamed.
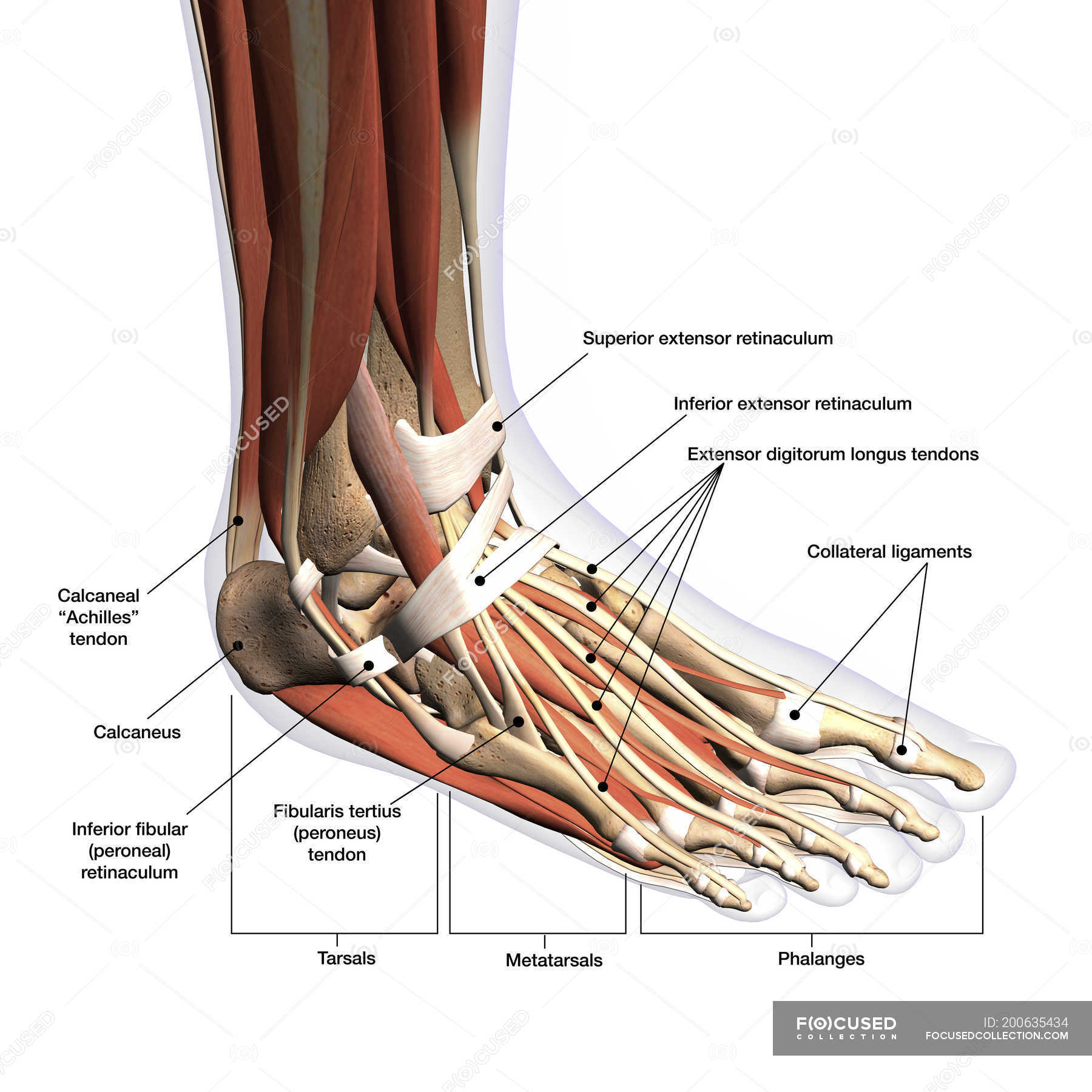
Anatomy of human foot with labels on white background — ankle, leg
The top bone of the foot is called the talus. It articulates with many of the other bones in the foot. Talus has three main parts: the body, the head and the neck. The body connects the talus to the lower leg. The head is adjacent to the navicular bone to form the talonavicular joint. The talonavicular joint is seen as the universal joint of.